- By A. CH.
- September 22, 2022
- Get Started Investing
Your Free Beginner’s Guide to ETF Investment
No time to spend searching for stocks? Looking for an easy way to invest your money that doesn’t require a financial analyst’s knowledge?
This beginner’s guide to ETF investment could be the solution!
This free beginner’s guide to ETF investment will cover what’s an ETF, the basics of ETF investment, stock vs ETF, ETF research, and how to buy an ETF.
Even though ETF is not a recent investment solution, it has seen a huge spike among retail investors recently. Simplicity, risk neutralization, and most importantly, time efficiency are a few of the benefits that an ETF investment can offer. This guide collects all the information that a beginner investor should know about ETF investment and we start with what’s an ETF. Let’s dive in!
In simple words, what’s an ETF?
Briefly, ETF investment is a conservative way of investment that doesn’t require full financial knowledge and it’s perfect for the beginner investor, who might not have the time or huge capital available for investment. Additionally, ETF investment is not limited to only beginner investors, as it’s considered simple diversification security for bigger portfolios and experienced investors too.
Specifically, investing in an ETF means that you’re investing in a pre-selected group of companies/assets that can be bought under one price. This price is calculated per piece/share.
Further, the price of any ETF is publicly available, as they are traded on stock exchanges, exactly like stocks.
This is how to describe an ETF in a simple way. However, there are more important things to know about ETF investment before you start investing. In this free ETF guide for beginner investors, we will cover the difference between ETF and stock investment, the different types of ETF, the most famous ETFs, how to structure your ETF research, and how to buy an ETF.

What ETF stands for?
ETF stands for Exchange Traded Fund (ETF).
In particular, ETF is a pool of companies designed by a financial company (Vanguard, Blackrock, Invesco, etc.). These companies list the ETF on a stock exchange (NYSE, LSE, etc). Similarly to stock, ETF is sold per share, so investors can buy any number of ETF shares anytime.
Overall, the price of an ETF share is defined by both the value of the fund’s holdings as well as supply and demand in the marketplace for the ETF (Source: iShares.com). Meaning the price goes up when many investors want to buy, and the price goes down when investors want to sell.
What’s the difference between ETF and Stocks?
In this section, we will see the three main differences between ETF and stock investment.
1. Cost
Firstly, stock investment requires the purchase of a full share, which is issued by a specific company. In ETF investment, you buy a bundle of many companies. Buying stocks separately can become very expensive, compared to buying an ETF.
2. Ownership
In the case of stock investment, you own a portion of a specific company. ETF doesn’t give you direct ownership of the company stock.
3. Level of Exposure
Additionally, ETF investment has less risk exposure than investing in stocks. Because ETF monitors a broader spectrum of companies, industries, or markets. Whereas, the stock investment is tied to specific companies.
Overall, these are the main three differences between stock and ETF investing that a beginner investor should know. Nevertheless, there are more things to know about ETF to get the full picture of what exactly an ETF is. Let’s take a look!
What are the different types of ETF?
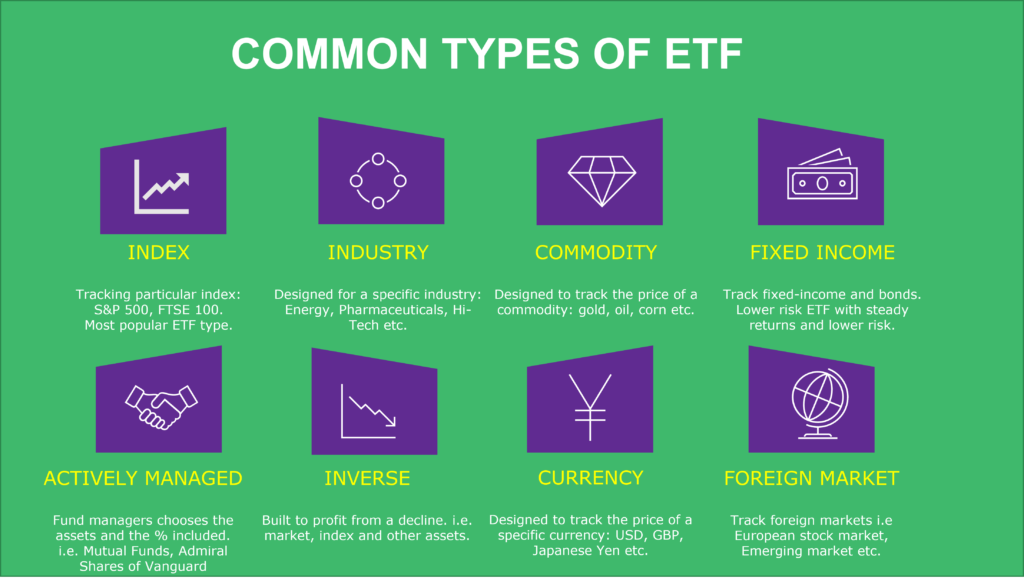
In general, there are a plethora of ETF options, which monitor: the oil and gas industry, wheat, precious metals, bonds and treasury bills, real estate, art, and more…
The eight most common types of ETF are:
- Index ETF (i.e S&P 500, Dow Jones industrial average, etc.)
- Industrial ETF (oil and energy industry, hi-tech industry, etc.)
- Commodity ETF (wheat, oil, corn, etc.)
- Fixed Income/Bond ETF
- Actively Managed ETF (Mutual Funds)
- Inverse ETF
- Currency Performance ETF (US dollar, Japanese Yen, Euro, etc.)
- Foreign Market ETF (European market ETF, Japanese market, emerging markets, etc.)
As this guide focuses on simplifying the ETF investment for beginner investors, we will emphasise the most common ETF type, which is the index ETF.
What’s an index ETF?
In short, indexes monitor the performance of a specific group of companies or assets (Investopedia). An index is a performance indicator, created and rated by financial rating agencies (Standard & Poor’s, Moodys, Fitch, etc.). Generally, Index ETF is the most popular ETF for beginners.
What an index does?
Tracks the performance of a country/market/industry/asset. Also, Index is an indication of the financial state of countries, markets, industries, and companies. Moreover, indexes can be investors, companies to make financial, investment, or business decisions.
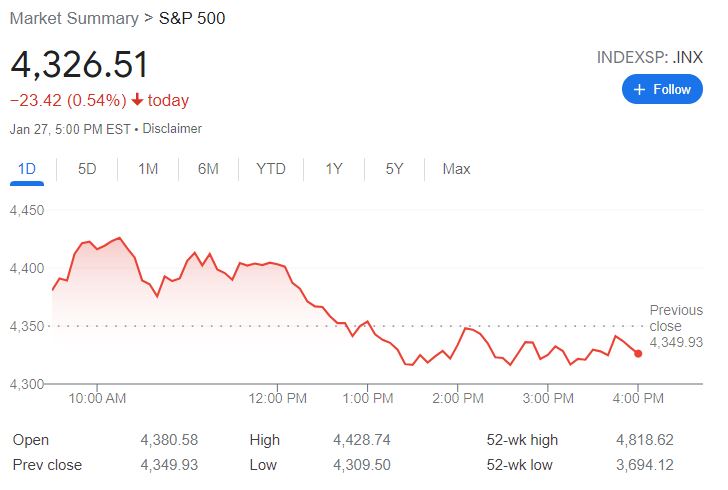
For instance, the performance of the top 500 biggest companies in the U.S are monitored by S&P 500 index Index. So by checking the S&P500, you can actually see the performance of the US market. Is the market going up or down?
Buying an index is not allowed, so ETF investing fulfils this investment desire. In simple words, when the index of the U.S market goes up, the ETFs, which track this particular market, will go up too. Therefore, the investor wins. Then investor decides to either sell their ETF shares or hold them for long-term investment.
Most famous indexes
There are many indexes available in the market, but these are the three most well-known based on the trading volume:
NASDAQ Composite: includes almost all stocks listed on the Nasdaq stock exchange.
SSE Composite Index: Also known as SSE Index is a stock market index of all stocks that are traded at the Shanghai Stock Exchange.
S&P 500: a world-known index, which tracks the 500 biggest companies in the United States.
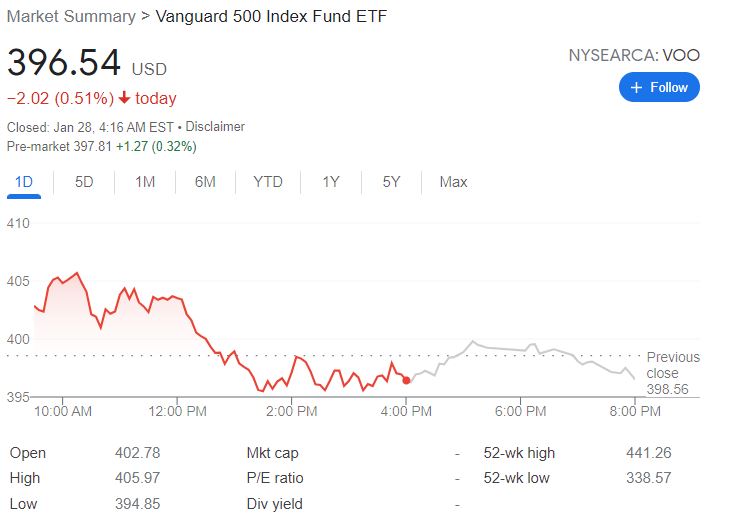
As shown in the graph below, the performance of the S&P 500 index is being mimicked by the S&P 500 ETF of Vanguard. Pay close attention to the line direction, it moves identically.
Things to be aware of before buying an ETF
If you have already read this full ETF guide, you should be in a very good place to understand what’s an ETF and the basics of ETF investment. Let’s learn some additional facts:
- – Index and ETF don’t have the same price.
- – ETFs are listed in a stock exchange, that’s why we call them Exchange Traded Funds.
- – Majority of ETFs have an annual expense ratio (expense ratio), which shrinks the return and this is how the issuing companies make their money.
- – Some ETFs might pay cash dividends, but not all!
- – ETF doesn’t need to be actively managed.
- – The issuing company might have two different types of the same ETF. Ask the difference between the two types before buying (ETF vs Mutual Fund).
- – ETF investment can outperform stock investment, if it’s done correctly (balance of costs, period of holding, and market of choice).
Obviously, this free ETF guide for beginner investors shouldn’t exclude the pros and cons of ETF. Read more here.
How to start searching and investing in an ETF?
Undoubtedly, ETF research can become a tiresome procedure as there are many types and options out there. The key to success is to be organised and have a step-by-step guide to navigate you through the ETF investment process. Before start checking for the price you will need to decide what type of ETF interests you the most, after that you need to follow the steps below:
- Decide which ETF type suits your investment style and portfolio.
- Research which companies offer the type of ETF you’re interested in.
- Create a comparison table of each ETF. Compare:
- Expenses vs Return
- Accessibility (Easily to buy, trade, monitor etc.)
- Performance
- Company trustworthiness (read reviews online or talk with your investment mentor)
- Speak with ETF company representatives or customer service, if you have any specific questions.
You can find financial information on financial media websites (Yahoo Finance, Market Watch, Morningstar …), Google, on Stock Exchange websites (S&P 500 => New York Stock Exchange, etc), and more.
Who are the ETF giants?
These are the biggest and most popular ETF issuing companies:
- Vanguard, the founding company of ETF investment (VOO, VTI, VXUS, etc.)
- iShares by Blackrock (EEM, IWM, FXI etc.)
- ProShares (TQQQ, SSO, BITO, etc.)
- SPDR (SPY, XBI, JNK, etc)
- Invesco (QQQ, BKLN, PDBC, etc.)
- and more …
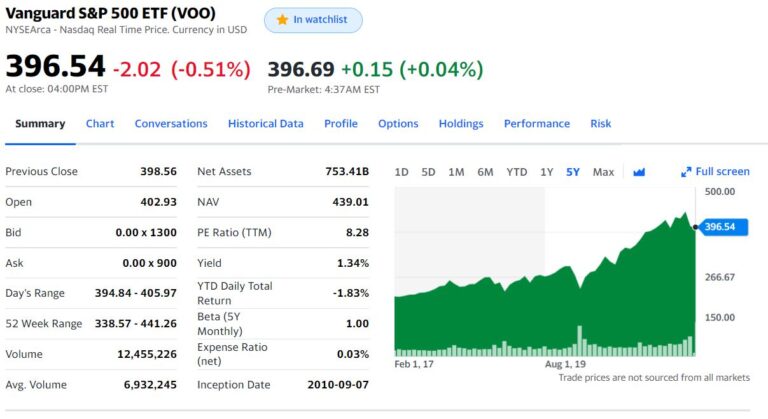
VOO, Vanguard’s S&P 500 ETF, is one of the most famous ETFs in the market. (Source: Yahoo Finance)
How can I buy an ETF?
These are the most common ways to buy an ETF:
- Directly from the ETF issuing company. Contact them either online or call the country representative office.
- Online Brokerages and Trading Platforms (webull, Robinhood, eToro, Ameritrade, etc.)
- Traditional Brokers
- Banks and more.
Finally, despite how simple the ETF investment sounds, it hides risks and negative returns like all investments. In conclusion, ETF investment is a good investment option for beginner and seasonal investors.
Hope this free beginner’s guide to ETF investment was useful. Feel free to get in touch and let us know.
Research and invest responsibly!
ACH



